Uncategorized
Calculating Overtime Pay in the United States

An employer who requires or permits an employee to work overtime is generally required to pay the employee premium pay for such overtime work. The last workweek is split and does not end in the current pay period. Payroll will calculate and pay overtime for this workweek in the next pay period. As can be readily seen from the above discussion, the correct calculation of overtime pay can be a difficult process depending on the number of different work arrangements an employer allows to exist in terms of basis of pay and hours worked. There are numerous opportunities for employers to make technical mistakes.
Other forms of compensation included in the regular rate
Under the FLSA, overtime pay is additional compensation (i.e., premium pay) that employers must pay to nonexempt employees who work more than 40 hours in a workweek. As previously stated, the federal rate is time and one-half the regular rate of pay, however, states that have their own laws may require daily overtime payments or double time premium pay. Sometimes nonexempt employees who are normally paid a fixed hourly rate work certain hours, usually at undesirable times, which grants them additional hourly pay. In such cases, employers must use the blended rate or weighted average of all rates paid in order to calculate the overtime premium due for hours worked over 40 in the workweek. Note that the FLSA has an exception to this rule that allows employer to pay overtime via the “rate in effect.” Most states, however, do not permit this method.
Decide which employees you need to pay overtime to
Some employers provide paid meal breaks when employees are relieved from their work duties. Bona fide meal breaks are not hours worked and these payments do not automatically convert the time to hours worked. The pay for these meal breaks may be excluded from the regular rate, unless an agreement or established practice indicates the parties have treated the time as hours worked, in which case the payments must be included in the regular rate. The specifics of overtime, including eligibility and rates, are governed by legal regulations in each country, designed to protect workers’ rights.
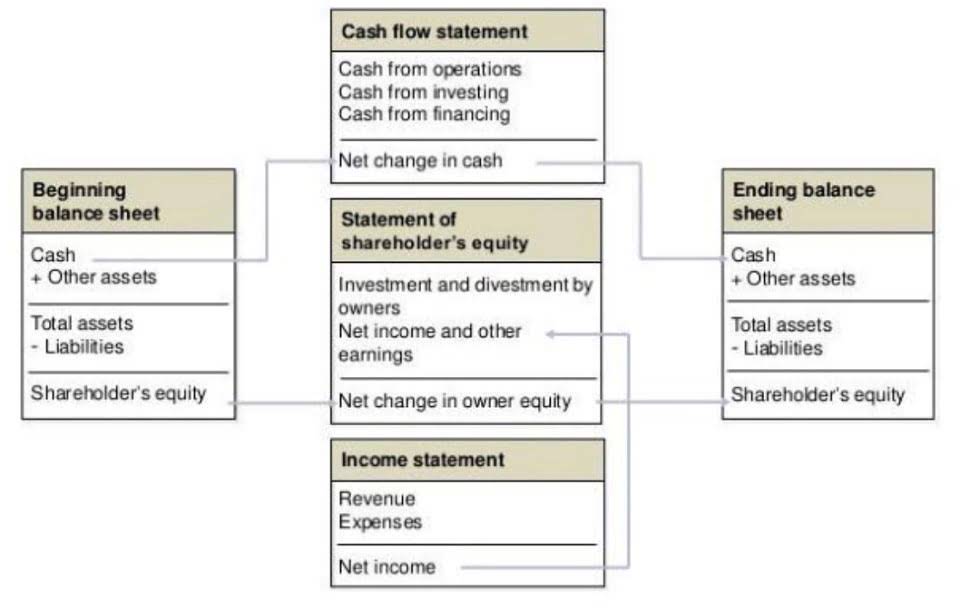
Step 3: Determine Total Nonovertime Compensation
- Payments made pursuant to a bona fide profit-sharing plan or trust or a bona fide thrift saving plan may be excluded from the regular rate.
- Otherwise stated, giving an employee the title of a manager staff does not necessarily make them managerial staff under Labor Law.
- By following the employment guidelines and calculation methods for overtime pay, workers can safeguard themselves against employers who miscalculate their pay or undercharge overtime rates.
- The amount of overtime pay due to an employee is based on the employee’s regular rate of pay and the number of hours worked in a workweek.
Employees in senior-level (SL) and scientific or professional (ST) positions who are paid under 5 U.S.C. 5376 are not excluded from the definition of “employee” in 5 U.S.C. 5541(2). Uma worked 46 hours on a first shift and five hours on a third shift during the same workweek. Her employer pays an additional $9 per hour premium for third-shift hours. A nonexempt employee with a fixed schedule earns a weekly salary of $400 and is expected to work 40 hours per week for that salary.

However, if the company follows a compressed workweek scheme, overtime pay may be given if the employee exceeds their agreed-upon schedule. Workplace policies should define the overtime hours your employer might expect and dictate the compensation you should receive. There are legislations in place to ensure fair treatment for employees and provide employers with clarity on the amount to pay employees for overtime. FLSA exempt employees, as defined in 5 U.S.C. 5541(2), who work full-time, part-time, or intermittent tours of duty are eligible for title 5 overtime pay.

Non-discretionary bonuses and commission payments
For information on what can be excluded from the regular rate calculation, see Overtime Calculator—Statutory Exclusions. The FLSA does not relieve an employer of any obligation it may have assumed by contract. However, how much is overtime pay an employee does not usually receive overtime pay nor premium pay because they are conditioned on whether overtime work was done or whether work was performed on a rest day or special non-working day. That is why in many companies, an overtime work form or a special work form is required to be filled-up by the employee and signed by his immediate supervisor as proof. Such compensation may be creditable toward overtime pay due under the FLSA.
Is overtime calculated by day or week?
Because the employee’s regular rate is already included in the straight time pay, we want to determine the additional overtime pay amount by taking the regular rate times 0.5 times the number of overtime (OT) hours. The https://www.facebook.com/BooksTimeInc regular rate is the rate at which overtime is calculated and includes more than just the employee’s normal salary or hourly, piece or daily rate. Generally, the regular rate encompasses all compensation provided to the employee as part of the individual’s employment, except for certain exclusions.
- Hence, an employee is entitled to his daily wage, 13th month pay, among others.
- For employees with rates of basic pay equal to or less than the rate of basic pay for GS-10, step 1, the overtime hourly rate is the employee’s hourly rate of basic pay multiplied by 1.5.
- Note that certain states have different methods for calculating the regular rate of pay for nonexempt employees who are paid on a salary basis.
- Different workweeks may be established for different employees or groups of employees.
- The time spent waiting to doff unique protective gear is also compensable because it is integral and indispensable to principal work activities, but the time spent waiting to don clothes was not found to be compensable time.
Calculate Regular Working Hours
- For example, if you normally pay an employee $25 an hour, this is their normal hourly rate.
- According to the Department of Labor, employees who make over $43,888 per year (effective July 1, 2024) or $58,656 (effective Jan. 1, 2025) are exempt from overtime.
- For example, some states have daily overtime pay requirements for hours worked in excess of eight hours in a day.
- All compensation paid by or on behalf of an employer to an employee as remuneration for employment must be included in the regular rate, whether paid in the form of cash or otherwise.
- Since the straight-time earnings have already been calculated (see Step 1), the additional amount to be calculated is one-half the regular rate of pay.
To make matters even more complex, businesses must comply with not only the FLSA, but also the wage and hour laws in state and local jurisdictions. When these regulations differ, employers have to apply the overtime pay rate that is most favorable to the employee. For employees with rates of basic pay equal to or less than the rate of basic pay for GS-10, step 1, the overtime hourly rate is the employee’s hourly rate of basic pay multiplied by 1.5. This document serves as a tool to help organizations calculate the regular rate for overtime purposes when a nonexempt employee receives shift differentials. A workweek is a period of 168 hours during 7 consecutive 24-hour periods. It may begin on CARES Act any day of the week and at any hour of the day established by the employer.
How do I calculate overtime from a basic salary?
Employee coverage, compliance with wage payment requirements and the application of most exemptions are determined on a workweek basis. Employees can be scheduled to work up to 40 hours per week as standard scheduling. If an employee works over 40 hours, he or she is working overtime hours and will be paid a higher rate for this time. The rate is one and a half times the hourly rate that the employee earns times the number of hours of overtime worked.
